What are Facial Veins?
Facial Veins are spider veins located on the face. They are also called Telangiectasias or Spider Angiomas. They are typically found on the cheeks, forehead, and nose. Spider veins on the face are easily treatable and usually present no additional signs. Although unflattering, facial veins do not typically indicate any serious underlying conditions. At Vein911® Vein Treatment Centers, we offer the best vein removal on the face, VeinGogh.
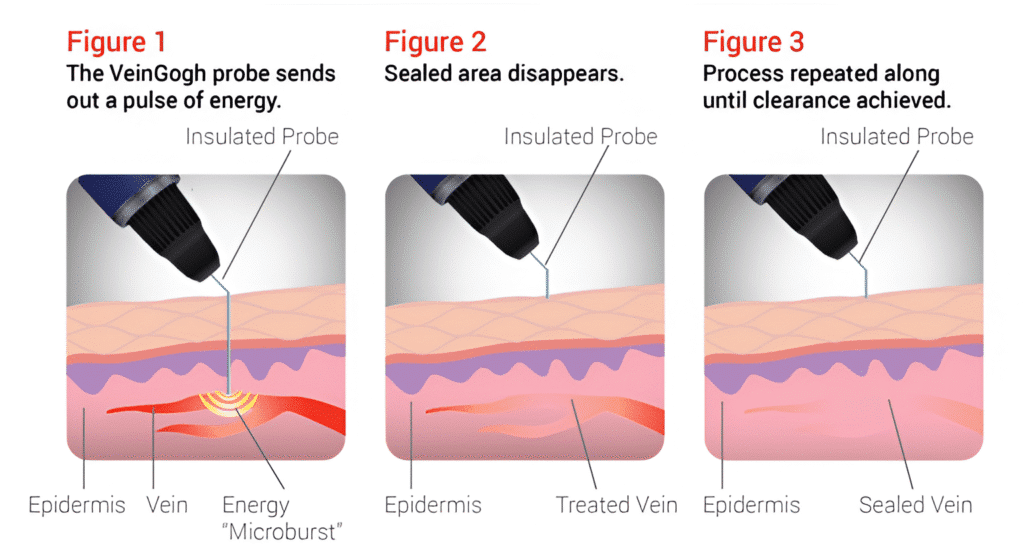
What is VeinGogh Treatment?
VeinGogh is the easiest way to reliably treat cosmetically unacceptable conditions of telangiectasia and spider veins. Unlike most lasers, VeinGogh can safely treat any skin type, including darker complexions. VeinGogh is a one of a kind treatment that incorporates Microburst Technology, which delivers a more effective and precise treatment, allowing us to really focus in on problem areas. VeinGogh vein removal magically eliminates those cosmetically disturbing spider veins and red spots permanently, and in just a few seconds. Full treatment is complete in less than 30 minutes and you can immediately leave our office without those red lines and spots. Your friends and family will wonder why you look 10-20 years younger!
A number of factors can cause veins on the face. Two of the most common are:
Sometimes, facial spider veins appear as a sign of rosacea, a skin condition that may cause redness, inflammation, acne, and oily skin to appear on the face. Rosacea is a progressive disorder Read more about Rosacea here.










